🔐 Access Control
PROMPT 2 uses role-based access control (RBAC) to manage user permissions throughout the system. This is implemented through Keycloak, which issues JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) and manages both system-wide and course-specific roles.
The platform distinguishes four main user types:
Administrator
Lecturer
Teaching Personnel
Student
Based on these, the system defines five roles, each with specific permissions:
🎓 Access Roles
Role |
Scope |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Prompt Administrator |
System-wide |
Full access to all courses, users, and settings. Handles configuration and maintenance. |
Prompt Lecturer |
System-wide |
Can create new courses and view student history across all past courses. |
Course Lecturer |
Course-specific |
Assigned when creating a course. Can configure course structure, manage phases, assess students, and assign final grades. |
Course Editor |
Course-specific |
Supports course execution. Can view participants and progress but cannot write data or assess students. May gain additional permissions per phase (e.g., give feedback). |
Course Student |
Course-specific |
Can apply to courses, participate in phases, and view their progress and grades. |
🧩 Role Resolution and Enforcement
The PROMPT 2 system distinguishes system-wide roles from course-specific roles.
🔐 System-Wide Roles: Prompt Administrator and Prompt Lecturer
These roles are managed directly in Keycloak and are encoded in each user’s JWT token. Any component (core or course phase service) can validate these roles by inspecting the token.
📘 Course-Specific Roles: Course Lecturer and Course Editor
These roles are dynamically created and linked to specific courses. The role names are generated with a naming convention that includes the semester and course name (e.g., ios25-iPraktikum-Lecturer). Because services typically operate using internal identifiers like courseID or coursePhaseID, they must map these IDs to role names.
To support this, the Core Server provides an endpoint that returns the correct role name for a given course or phase ID. Services can then:
Request the role name using the ID
Check whether the user’s JWT contains the required role
Cache the result, since mappings rarely change
🧪 Example: Course Lecturer Access Flow
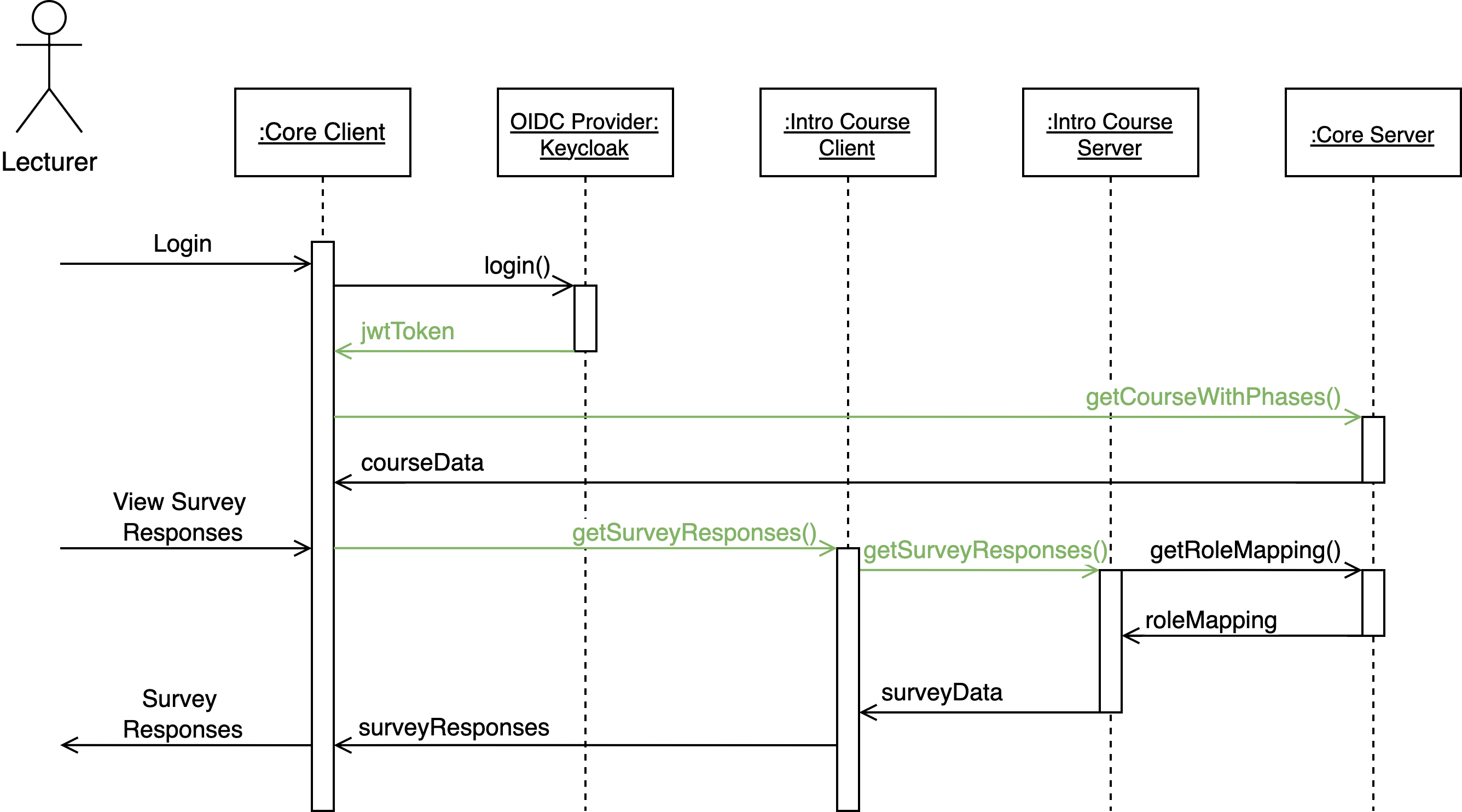
In this flow:
A lecturer logs in through the Core Client, which authenticates via Keycloak.
Keycloak issues a JWT token, which the client uses to retrieve associated courses from the Core Server.
When the lecturer accesses a course phase (e.g., the Intro Course), the microfrontend sends a request to the respective course phase service.
This request includes the
jwtTokenandcoursePhaseID.The course phase service contacts the Core Server to resolve the
coursePhaseIDinto a role name.It checks the JWT for the corresponding role before allowing access.
Note: This role mapping is public and not user-specific. Therefore, it does not require authentication and can be cached safely.
👩🎓 Student Role and Phase Participation
The Course Student role is handled differently. Because student access is phase-dependent and students progress from phase to phase dynamically, their membership cannot be captured in static Keycloak roles.
Instead, the Core Server maintains authoritative information about which students are allowed in which phases. Course phase services must verify student membership using the dedicated Core endpoint.
🧪 Example: Course Student Access Flow
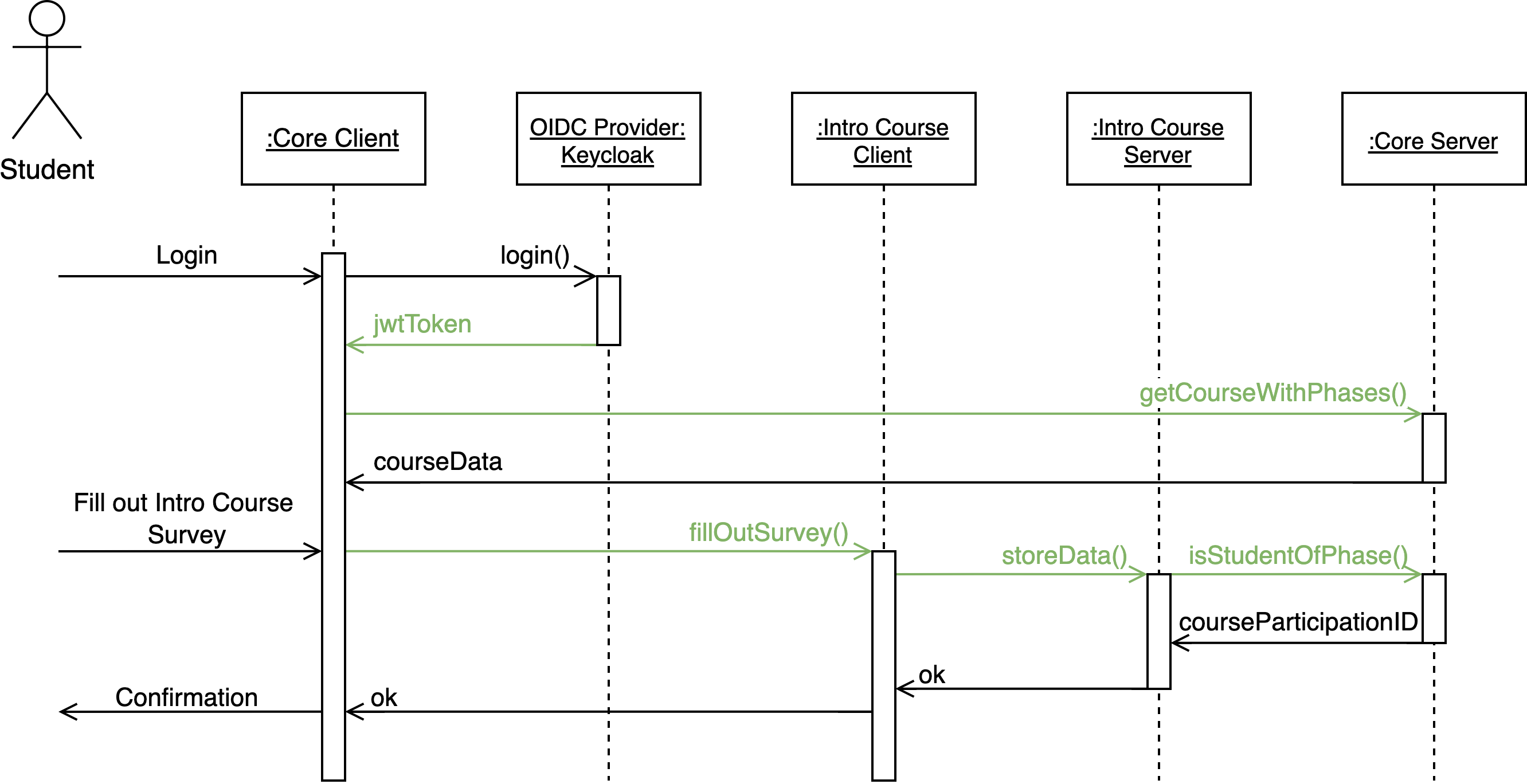
In this flow:
A student logs in and receives a JWT token from Keycloak.
The Core Client only shows courses and phases the student is currently enrolled in.
When accessing a course phase (e.g., a survey in the Intro Course), the phase service:
Sends the
jwtTokenandcoursePhaseIDto the Core ServerCore verifies that the student is part of the phase
Returns the
courseParticipationIDThe phase service uses this ID to record progress (e.g., survey response)
Because phase participation may change (e.g., after passing a phase), the membership check result should not be cached long-term.
🎯 Custom Roles for Fine-Grained Access
PROMPT 2 also supports the creation of custom Keycloak roles for advanced access scenarios. Instructors can define roles for specific course phases and assign them to users as needed.
These custom roles:
Do not inherit permissions from system-defined roles
Can be used by phase services to define access levels such as team membership or feedback permissions
Example: A course phase service may define team roles (team-1, team-2) and use them to differentiate student permissions within a team-based project.
✅ Summary
Role Type |
Defined In |
Scope |
Validated Using |
|---|---|---|---|
Prompt Administrator |
Keycloak |
System-wide |
JWT inspection |
Prompt Lecturer |
Keycloak |
System-wide |
JWT inspection |
Course Lecturer |
PROMPT Core |
Per Course |
Mapped role + JWT |
Course Editor |
PROMPT Core |
Per Course |
Mapped role + JWT |
Course Student |
PROMPT Core |
Per Phase |
Membership endpoint |
Custom Role |
Keycloak |
Custom Logic |
Service-defined usage |